Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithm based on Regularity
Qingfu Zhang, Aimin Zhou, Yaochu Jin, “RM-MEDA: A Regularity Model Based Multiobjective Estimation of Distribution Algorithm”, IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 41-63, 2008. [MATLAB code] [C++ code] [Erratum to Figure 20]
Abstract: Under mild conditions, it can be induced from the Karush-Kuhn-Tuckercondition that the Pareto set, in the decision space, of a continuous multiobjective optimization problem is 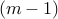 -D piecewise continuous, where
-D piecewise continuous, where 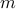 is the number of objectives. Based on this regularity property, we propose a Regularity Model based Multiobjective Estimation of Distribution Algorithm (RM-MEDA) for continuous multiobjective optimization problems with variable linkages. At each generation, the proposed algorithm models a promising area in the decision space by a probability distribution whose centroid is a
is the number of objectives. Based on this regularity property, we propose a Regularity Model based Multiobjective Estimation of Distribution Algorithm (RM-MEDA) for continuous multiobjective optimization problems with variable linkages. At each generation, the proposed algorithm models a promising area in the decision space by a probability distribution whose centroid is a 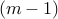 -D piecewise continuous manifold. The Local PCA algorithm is used for building such a model. New trial solutions are sampled from the model thus built. A non-dominated sorting based selection is used for choosing solutions for the next generation. Systematic experiments have shown that, overall, RM-MEDA outperforms other three state-of-the-art algorithms, GDE3, PCX-NSGA-II and MIDEA, on a set of test instances with variable linkages. We have demonstrated that, compared with GDE3, RM-MEDA is not sensitive to algorithmic parameters, and has good scalability to the number of decision variables in the case of nonlinear variable linkages. A few shortcomings of RM-MEDA have also been identified and discussed in this paper.
-D piecewise continuous manifold. The Local PCA algorithm is used for building such a model. New trial solutions are sampled from the model thus built. A non-dominated sorting based selection is used for choosing solutions for the next generation. Systematic experiments have shown that, overall, RM-MEDA outperforms other three state-of-the-art algorithms, GDE3, PCX-NSGA-II and MIDEA, on a set of test instances with variable linkages. We have demonstrated that, compared with GDE3, RM-MEDA is not sensitive to algorithmic parameters, and has good scalability to the number of decision variables in the case of nonlinear variable linkages. A few shortcomings of RM-MEDA have also been identified and discussed in this paper.
Aimin Zhou, Qingfu Zhang and Yaochu Jin, “Approximating the Set of Pareto Optimal Solutions in Both the Decision and Objective Spaces by an Estimation of Distribution Algorithm”, IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 1167-1189, 2009. [C++ code]
Abstract: Most existing multiobjective evolutionary algorithms aim at approximating the Pareto front (PF), which is the distribution of the Pareto-optimal solutions in the objective space. In many real-life applications, however, a good approximation to the Pareto set (PS), which is the distribution of the Paretooptimal solutions in the decision space, is also required by a decision maker. This paper considers a class of multiobjective optimization problems (MOPs), in which the dimensionalities of the PS and the PF manifolds are different so that a good approximation to the PF might not approximate the PS very well. It proposes a probabilistic model-based multiobjective evolutionary algorithm, called MMEA, for approximating the PS and the PF simultaneously for an MOP in this class. In the modelling phase of MMEA, the population is clustered into a number of subpopulations based on their distribution in the objective space, the principal component analysis technique is used to estimate the dimensionality of the PS manifold in each subpopulation, and then a probabilistic model is built for modeling the distribution of the Pareto-optimal solutions in the decision space. Sucha a modeling procedure could promote the population diversity in both the decision and objective spaces. MMEA is compared withthree other methods, KP1, Omni-Optimizer and RM-MEDA, on a set of test instances, five of which are proposed in this paper. The experimental results clearly suggest that, overall, MMEA performs significantly better than the three compared algorithms in approximating both the PS and the PF